

- #Higher order sequences math how to#
- #Higher order sequences math pdf#
- #Higher order sequences math trial#
- #Higher order sequences math series#
Prerequisite: either a minimum grade of 2.0 in MATH 136. for students wanting to explore mathematical thinking at a higher level. Second year of an accelerated two-year sequence prepares students for senior-level mathematics courses.
#Higher order sequences math pdf#
This just means that the nth term, U n is equal to 2 × the (n-1)th term, U n-1.Download a PDF of the paper titled Higher Order Fibonacci Sequences from Generalized Schreier sets, by Hung Viet Chu and 2 other authors Download PDF Abstract: A Schreier set $S$ is a subset of the natural numbers with $\min S\ge |S|$. Prerequisites: Sophomore standing and one previous university math course. So to define the recurrence relation, we give the first term, written U 1 = 2. Each term in the sequence is got by doubling the previous term.
#Higher order sequences math how to#
Then you give a formula to tell you how to work out the next term from the previous ones.įor example, consider the sequence: 2, 4, 8, 16, 32. Abstract: We define a notion of higher order renormalization group equation and investigate when a sequence of trees satisfies such an equation. To define a recurrence relation, you have to give the first term. This is where the next term of a sequence is defined using the previous term(s).
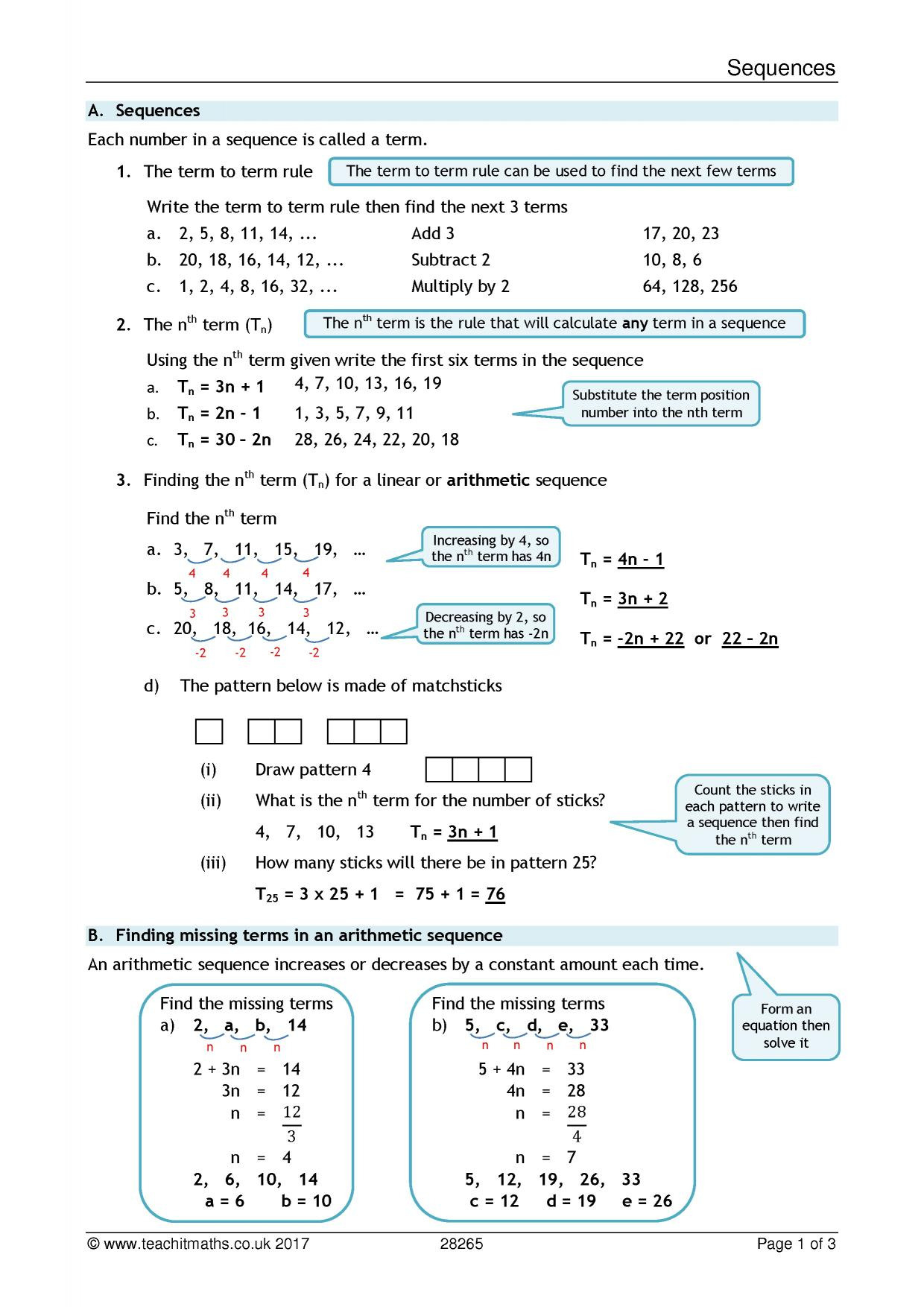
a procedural parameter, which is a parameter of a procedure that is itself a procedure), returns a function as its result. converges (gets closer and closer) towards the limit zero. In mathematics and computer science, a higher-order function (HOF) is a function that does at least one of the following: takes one or more functions as arguments (i.e. Project Maths Development Team 2009 www.projectmaths.
#Higher order sequences math series#
Sequences whose nth term approaches a finite number as n becomes larger are known as convergent sequences and the number to which the sequence converges is known as the limit of the sequence. That the student knows not all sequences and series are arithmetic. The 5th term is therefore U 5 = 25 + 1 = 26. If the rule is to add or subtract a number each time, it is called an arithmetic sequence. The number of ordered elements (possibly infinite) is called the length of the sequence. 1 2 3 4 5 Sequences Number sequences are sets of numbers that follow a pattern or a rule. Like a set, it contains members (also called elements, or terms). Arithmetic sequences are also known as linear sequences because, if you plot the position on a horizontal axis and the term on the vertical axis, you get a. sequence that obtained an AP test score of 4 or higher on the calculus AB. en we establish several new and interesting identi ties relating to the in nite and ni te sums.
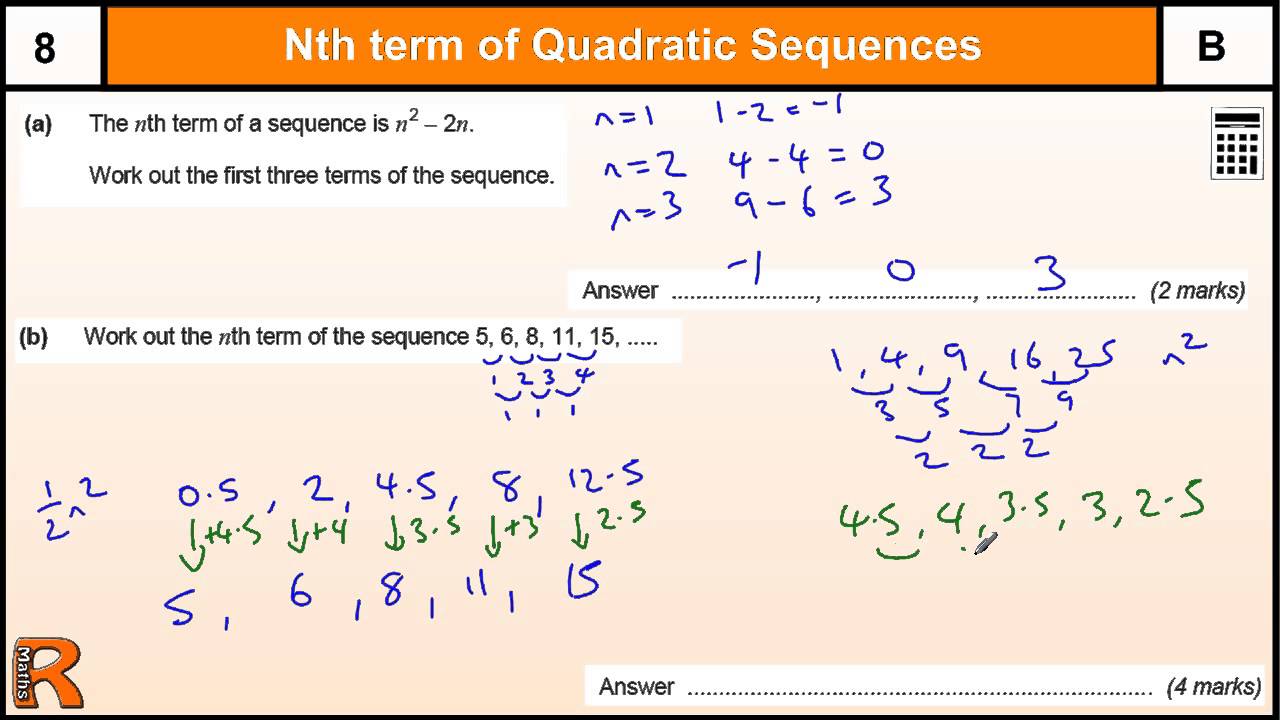
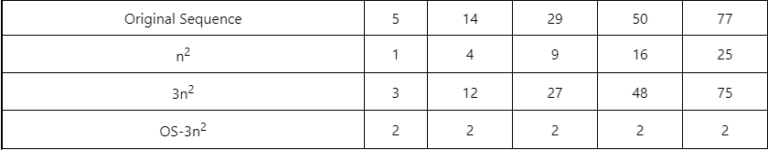
Using each of these equations, in the order theyre stated here. to study the reciprocal sums of higher power of higher-order sequences. The nth term of a sequence is sometimes written as U n. Mathematical Sequences (sourced from Wikipedia) In mathematics, informally speaking, a sequence is an ordered list of objects (or events). Note: MATH 173-MATH 174 must be taken in order but MATH 164 and MATH 165 can. looking at the first and second differences of this sequence would look like. Also, the triangular numbers formula often comes up. In many cases, square numbers will come up, so try squaring n, as above. 3, 6, 9, 12.), there will probably be a three in the formula, etc. Tips: if the sequence is going up in threes (e.g. For some sequences, there is no easy way of working out the nth term of a sequence, other than to try different possibilities. This is the required sequence, so the nth term is n² + 1.
#Higher order sequences math trial#
Let"s use trial and error (essentially guessing what we think will work): What is the nth term of the sequence 2, 5, 10, 17, 26. To find the 1st term, put n = 1 into the formula, to find the 4th term, replace the n"s by 4"s: 4th term = 2 × 4 First- and second-order equations special functions Laplace transform solutions higher order equations Fourier series partial differential equations. Such sequences can be expressed in terms of the nth term of the sequence. A-Level Maths revision looking at Sequences including Notation, Convergent Sequences and Recurrence Relations.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
